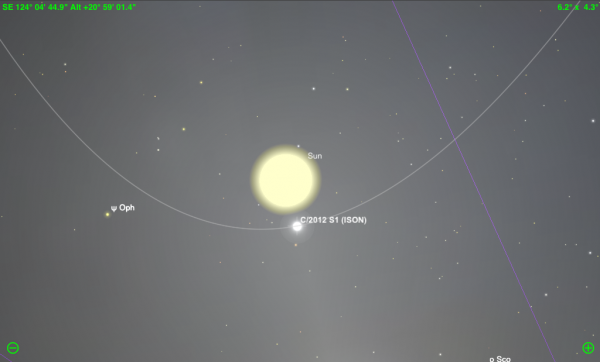
Today comet C/2012 S1 ISON will pass through perihelion, its closest approach to the Sun.
At a mere 1,800,000km (1,100,000miles) this will be a close pass indeed. As perihelion is measured from center to center, the distance is even closer if you consider the 695,500km (432,200mile) radius of the Sun. Subtracting the solar radius you realize the comet will pass a mere 1,100,000km (680,000miles) above the surface of the Sun. At this distance the intensity of the solar radiation will be nineteen thousand times more intense than a sunny day on Earth. Hot indeed!!

At closest approach the comet will be less than a degree from the Sun, difficult to pick out. An observers best bet will be as it approaches and as it moves away from the solar disk. As the comet nears perihelion it will approach the Sun from the west, best seen in the dawn sky. After perihelion it will exit the Sun’s vicinity to the north, favoring northern hemisphere observers.
The comet should be spectacular in the cameras of the dedicated solar observation satellites. Check out the real time views from SOHO or Stereo.