I understand it was quite the scramble, but both telescopes are back on-sky tonight.
The earthquakes started just after two this afternoon with the magnitude 4.5 event that got our attention so quickly. This gave day crew three hours to have everything inspected, checked out and ready for the night. Physical inspections, instrument checkouts, and more, an extensive checklist to follow and insure that no real damage was done by the temblors. Just after 5pm we got word that everything was good-to-go and both telescopes would be released for the night’s observing.
As of writing this, about ten hours after the first quake, there have been 32 separate events under Mauna Kea detected by the seismographs. A half dozen of those were near magnitude three. I have felt thirteen separate aftershocks, this plus the original quake makes fourteen, the most I have ever felt in a single day by a wide margin.
The USGS has released a statement noting that this was probably a “structural adjustment” a result of the enormous weight of Mauna Kea stressing the underlying rock…
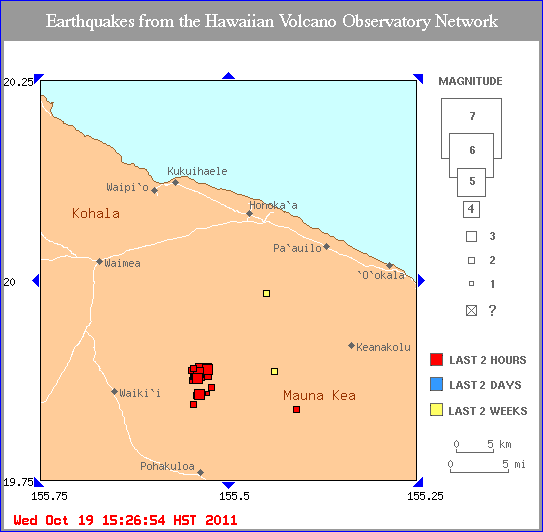
Magnitude 4.5 earthquake on the north flank of Mauna Kea
By USGS/HVO
Hawai‘i Island, HAWAII—The U.S. Geological Survey’s Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) recorded a magnitude-4.5 earthquake located beneath the Island of Hawai‘i on Wednesday, October 19, at 2:10 p.m. HST. This earthquake was centered about 9 km (6 mi) northwest of Mauna Kea’s summit and 49 km (31 mi) west-northwest of Hilo, at a depth of 18.7 km (11.6 mi).
The earthquake was widely felt on the Island of Hawai’i. The USGS “Did you feel it?” Web site (http://earthquake.usgs.gov/eqcenter/dyfi/) received more than 500 felt reports within an hour of the earthquake.
The earthquake was the largest in a cluster of about 20 earthquakes on the north flank of Mauna Kea on Wednesday afternoon. Most of these aftershocks were too small to be felt, but, as of 3:30 p.m., two earthquakes with magnitudes greater than 3.0 had occurred in addition to the magnitude-4.5 event.
Over the past 25 years, the north flank of Mauna Kea has experienced 10 earthquakes greater than magnitude 4.0, including today’s event, at depths of 10–40 km (6–25 mi). Deep earthquakes in this region are most likely caused by structural adjustments within the Earth’s crust due to the heavy load of Mauna Kea.
Adjustments beneath Mauna Kea during past similar events, such as in March 2010, have produced a flurry of earthquakes, with many small aftershocks occurring for days after the main quake. Given this history, it is possible that additional small earthquakes may be recorded in the coming days.
Today’s earthquakes caused no detectable changes on the continuing eruption of Kilauea Volcano.
For eruption updates and information on recent earthquakes in Hawai’i, visit the Hawaiian Volcano Observatory website at http://hvo.wr.usgs.gov